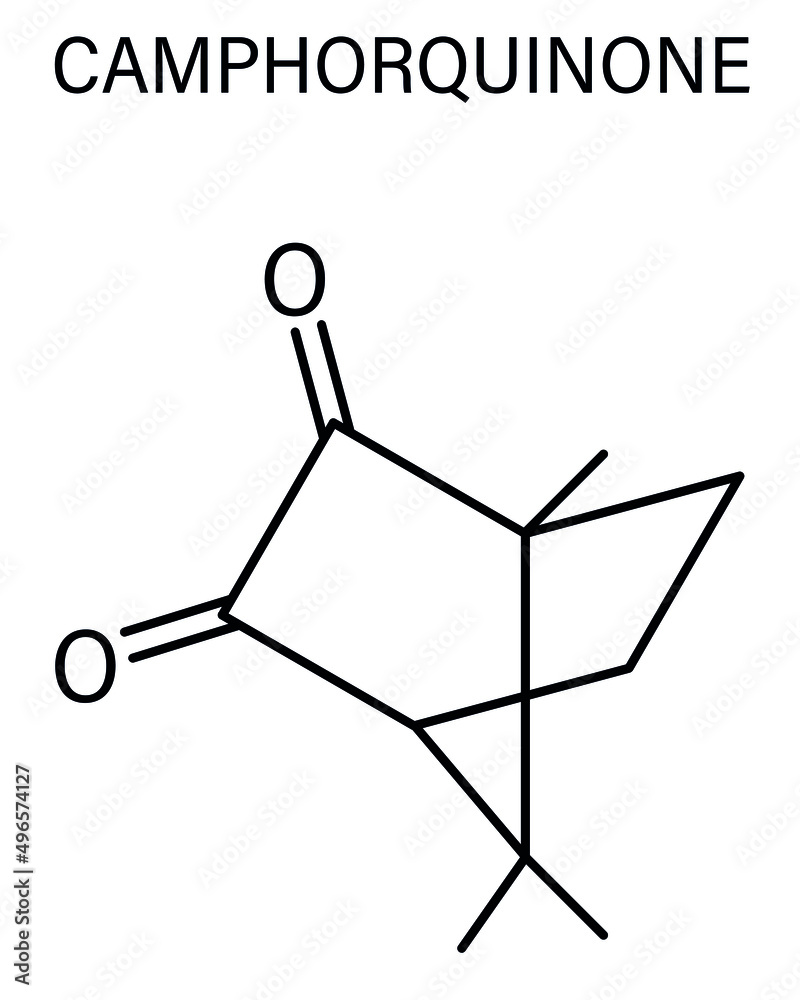
Camphorquinone, also known as 2,3-bornanedione, is an organic compound derived from camphor. A yellow solid, it is used as a photoinitiator in curing dental composites. Camphorquinone is produced by the oxidation of camphor with selenium dioxide.
Photocuring details
Polymerization is induced very slowly by camphorquinone, so amines such as N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine, 2-ethyl-dimethylbenzoate, N-phenylglycine are generally added to increase the rate of curing.
It absorbs very weakly at 468 nm (extinction coefficient of 40 M−1·cm−1) giving it a pale yellow color. Photoexcitation results in nearly quantitative formation of its triplet state through intersystem crossing and very faint fluorescence.
Reactions
It can be hydrolyzed by the enzyme 6-oxocamphor hydrolase.
Camphorquinone has been examined as a reagent in organic synthesis.
References